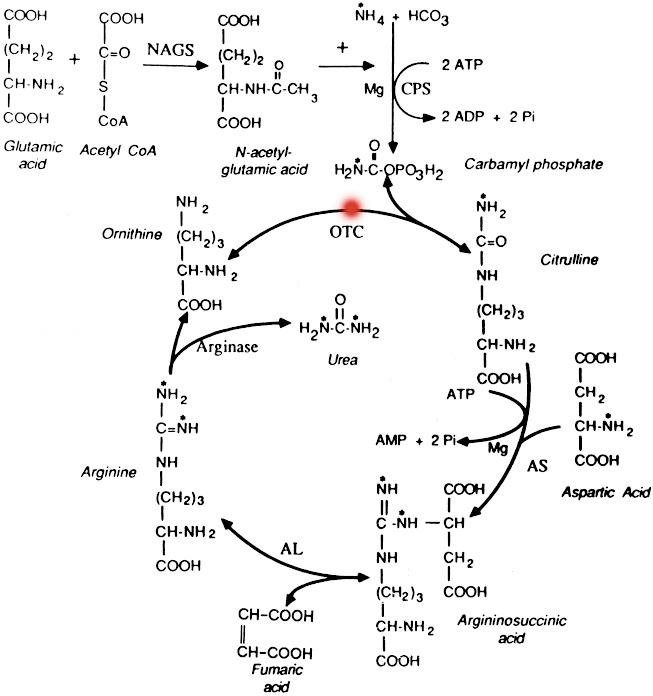
Late-Onset OTC Deficiency
Ornithine carbamoyl transferase deficiency is a frequent enzymatic disorder transmitted either as a recessive or dominant X-linked trait. Mutations with no residual enzyme activity are always expressed in hemizygote males by a very severe neonatal hyperammonemic coma that generally proves to be fatal. Heterozygous females are either asymptomatic or express orotic aciduria spontaneously or after protein intake. This identifies carriers. Females may also be affected by symptoms with various degrees of intensity, ranging from dislike for proteins to chronic vomiting, growth retardation, hypotonia, psychomotor retardation, hyperammonemic coma, or psychiatric disorders. In females, outcome is extremely variable, depending on the degree of inactivation of the muted X chromosome. Mutations leading to residual enzyme activity result in juvenile or even adult hyperammonemic coma in males, simulating Reye's syndrome or encephalitis. Females remain always asymptomatic. (Source: Orphanet)